The tomography showed that the bone tissue was at the level of the enamel-cementum junction and that the gingival tissue covered part of the anatomic crown (Figure 1(b)).Virtual planning was also performed using DSD, which showed the need to increase the size of the clinical crowns for better aesthetics (Figure 1(c)).With these data, it was shown that the patient suffered from altered passive.. The term "crown" is used in various ways, so it may help differentiate them. Clinical crown: The visible region of your teeth not covered by your gums, including your visible enamel-covered anatomic crowns and visible root. Anatomic crown: The top portion of your teeth is covered in enamel, including parts covered by your gums.
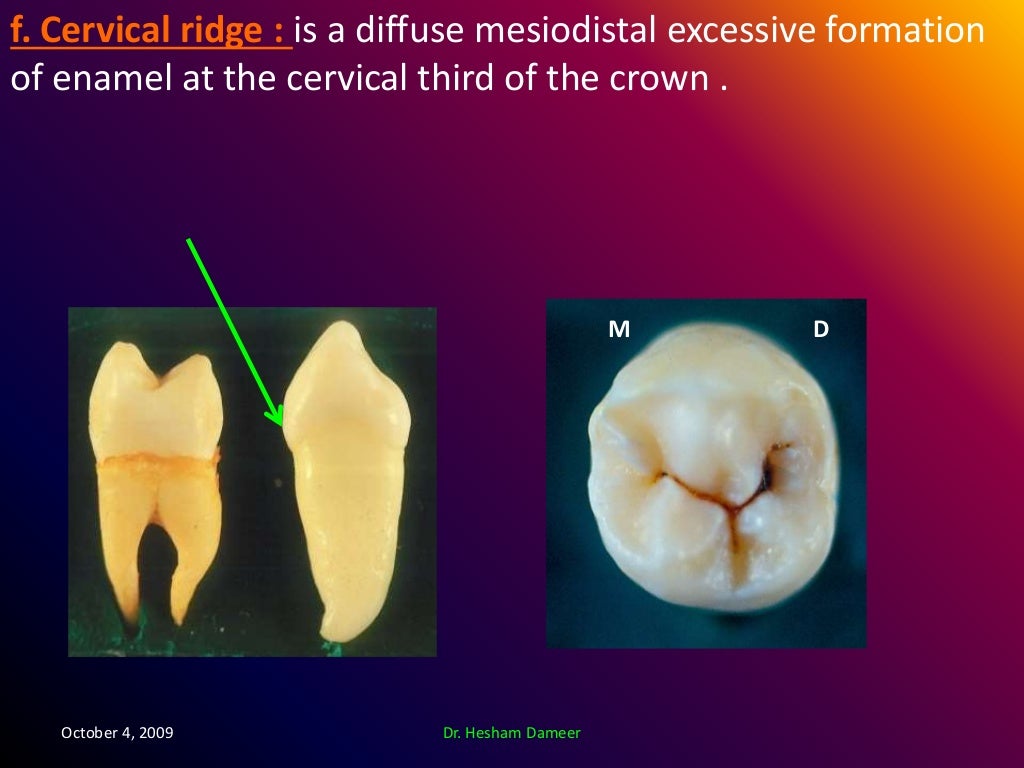
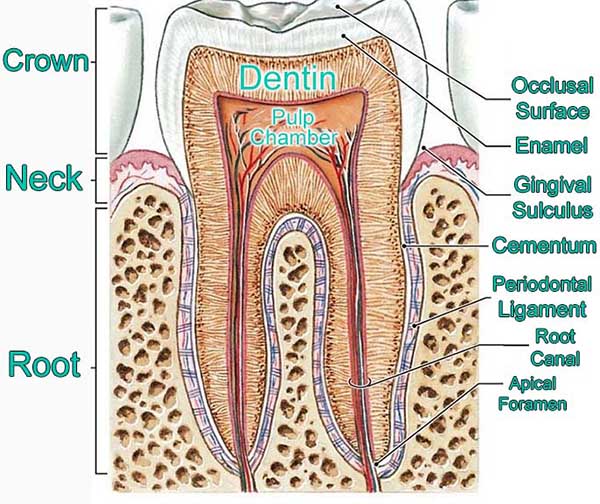
Anatomical landmarks of the crown

Clinical view of definitive crown. Download Scientific Diagram

Photo Gallery Chow Periodontics
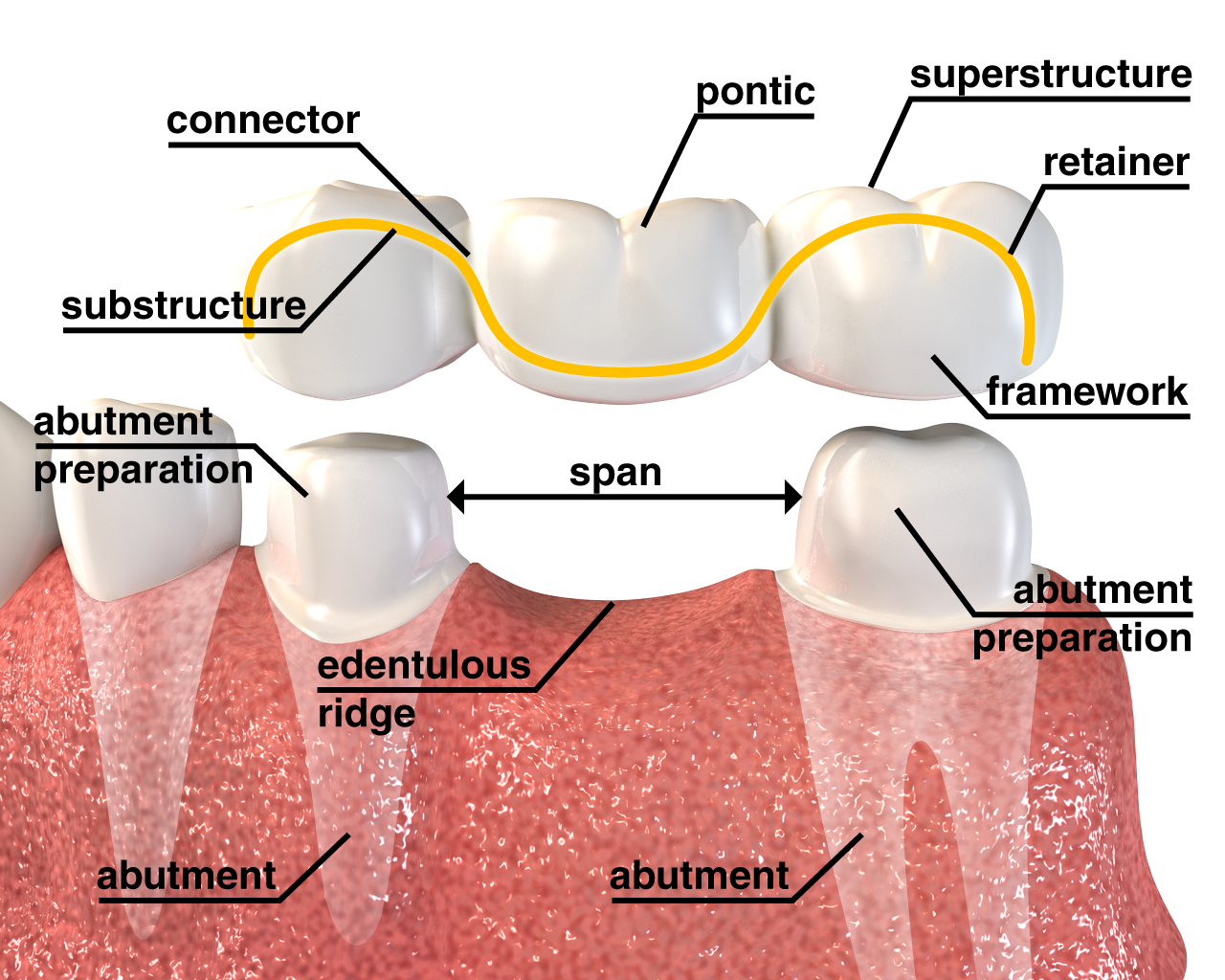
Dental Crowns & Bridges Monarch Dental Clinic, Vadodara
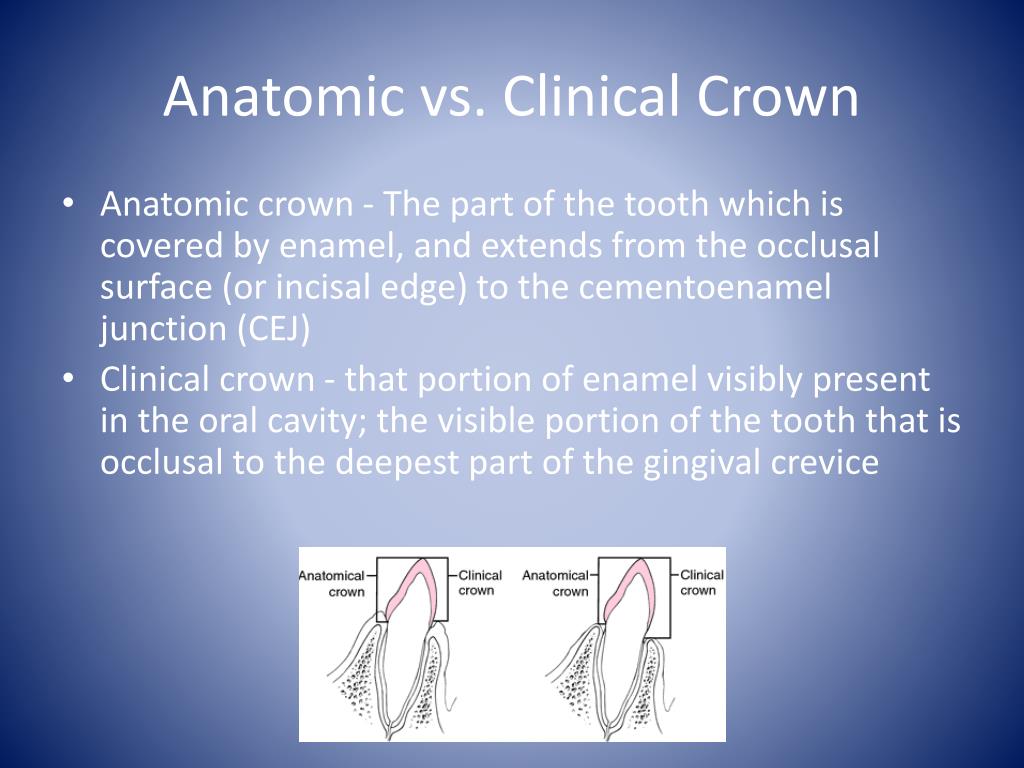
PPT Dental Terminology PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1897364

Difference between Anatomical & clinical crown?? Dental, Anatomical, Clinic
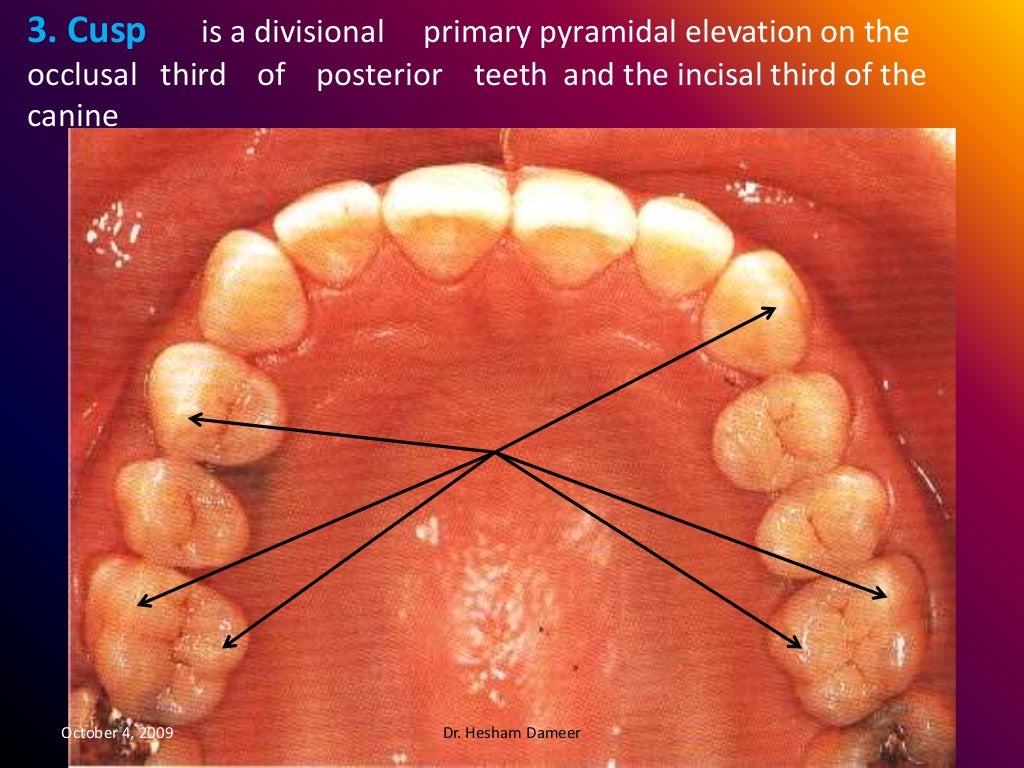
Anatomical landmarks of the crown

Esthetical Clinical Crown Lengthening, Lip Repositioning, and Gingival Depigmentation Plastic
Introduction
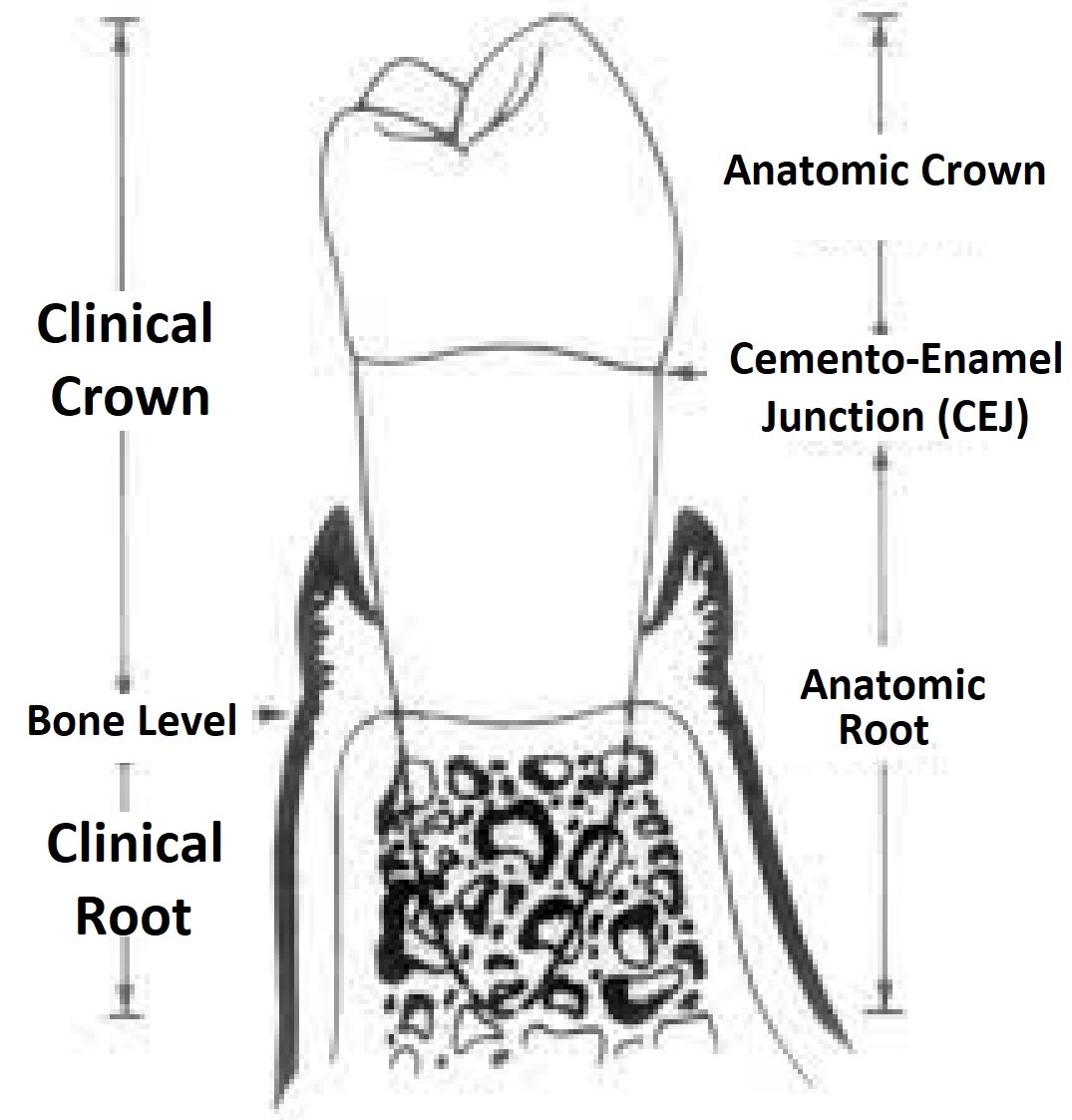
What is crowntoroot ratio? News Dentagama

Dental anatomy landmark part 1 YouTube

Clinical Crown Lengthening YouTube
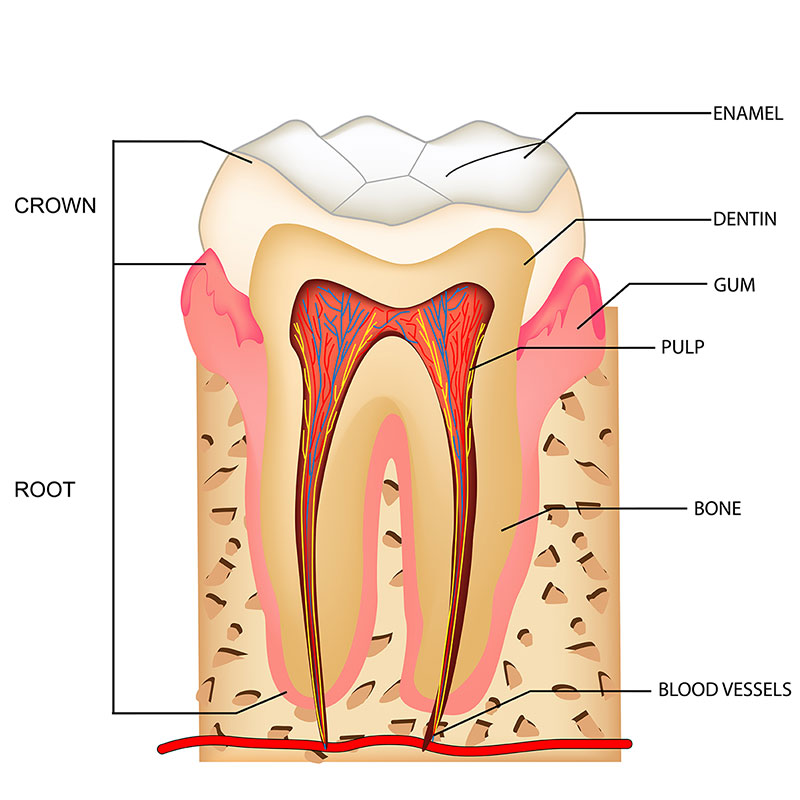
ToothAnatomy Serene Smiles

Regency Dental Group Dental Clinical Terms Anatomical Crown

Child and Adult Dentition (Teeth) Structure Primary Permanent TeachMeAnatomy

Scanning for Full Anatomical Crown YouTube

Anatomical Crown and Root vs Clinical Crown and Root YouTube
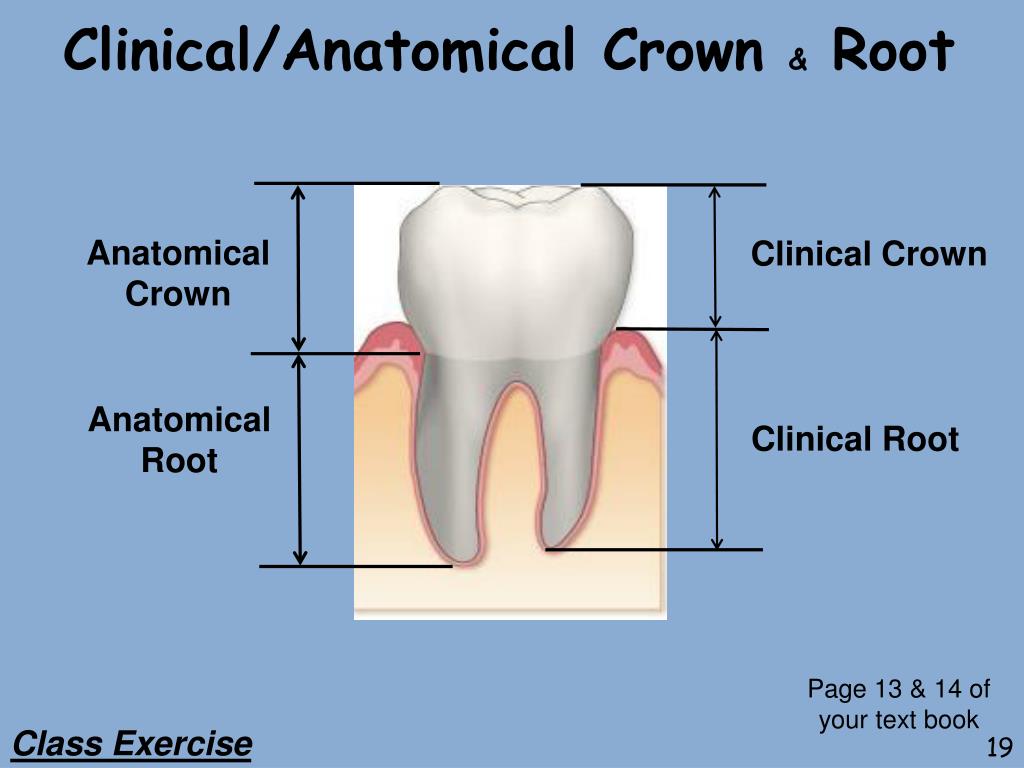
PPT Dental Terminology Part 2 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6706096

How to design a full anatomical crown YouTube
Tooth Anatomy Carson & Carson, DDS
An excessive amount of maxillary gingival display, concomitant with short clinical crowns, is generally regarded as unpleasing during smiling, having a negative personal and social impact. 1,2.. Crown contours represent a group of char acteristics critical to the longevity and success of any dental restoration. The contours of concern are the proximal sur faces, interproximal contacts, marginal ridges, facial and lingual convexities, and anterior lingual concavities. In restoring the gingival third of a crown, a flat emergence profile.